Americans in Their Prime Are Flooding Into the Job Market
Share of people between 25 and 54 working or seeking jobs rose this year to highest level since 2002
The core of the American labour force is back.
Americans between 25 and 54 years of age are either employed or looking for jobs at rates not seen in two decades, a trend helping to counter the exodus of older baby boomers from the workforce. Economists define that age range as in their prime working years—when most Americans are done with their formal education, aren’t ready to retire and tend to be most attached to the labor force.
In the first months of the pandemic, nearly four million prime-age workers left the labor market, pushing participation in early 2020 to the lowest level since 1983—before women had become as much of a force in the workplace. Prime-age workers now exceed pre pandemic levels by almost 2.2 million.
That growth is taking a little heat out of the job market and could help the Federal Reserve’s efforts to tamp down inflation by keeping wage growth in check.
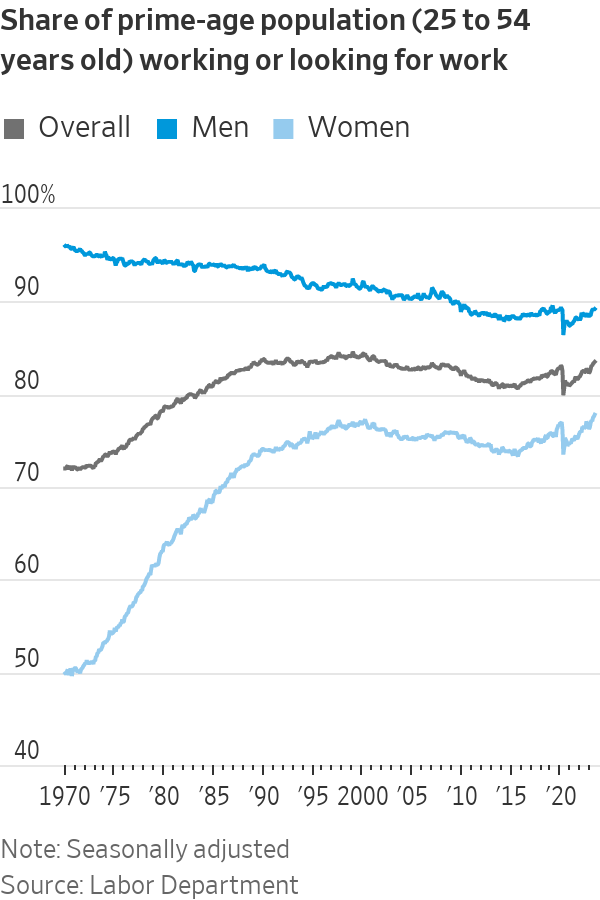
Women lead the way
The resurgence of mid career workers is driven by women taking jobs.
The labor-force participation rate for prime-age women was the highest on record, 77.8% in June. That is well up from 73.5% in April 2020.
Men, however, tend to be employed at higher rates. The overall prime-age participation rate rose in June to 83.5%, the highest since 2002.
The big draw: a tight labor market. The unemployment rate has hovered near a half-century low for more than a year, and job openings outnumber the ranks of unemployed. Employers can’t be as choosy or selective, William Rodgers, vice president and director of the Institute for Economic Equity at the St. Louis Fed, said earlier this month.
Employers “are more apt to be willing to work with candidates—in this case it’s working with moms, or parents in general,” he said. “Tight labor markets can help to punish those who discriminate in hiring and compensation.”
Other factors are also at play. Women aren’t having as many children—there were about 3.66 million births in 2022, 655,000 fewer than the peak in 2007—so child-care responsibilities have decreased.
Julia Pollak, chief economist at ZipRecruiter, said it is possible for women’s participation to rise further if employers adopt or the government requires additional family-friendly policies. U.S. female participation lags behind that of other industrialised economies in part because of the cost of child care, which is subsidised elsewhere.
Rising wages lure workers, counter demographic shifts
Employers raised wages, offered employees more flexibility and improved benefits in recent years.
Average wage gains remain elevated this year and have recently surpassed inflation. And Americans are logging more hours of work from home than they did before the pandemic.
Employer recruitment efforts helped offset some broader demographic shifts, including an ageing population and rise in retirements.
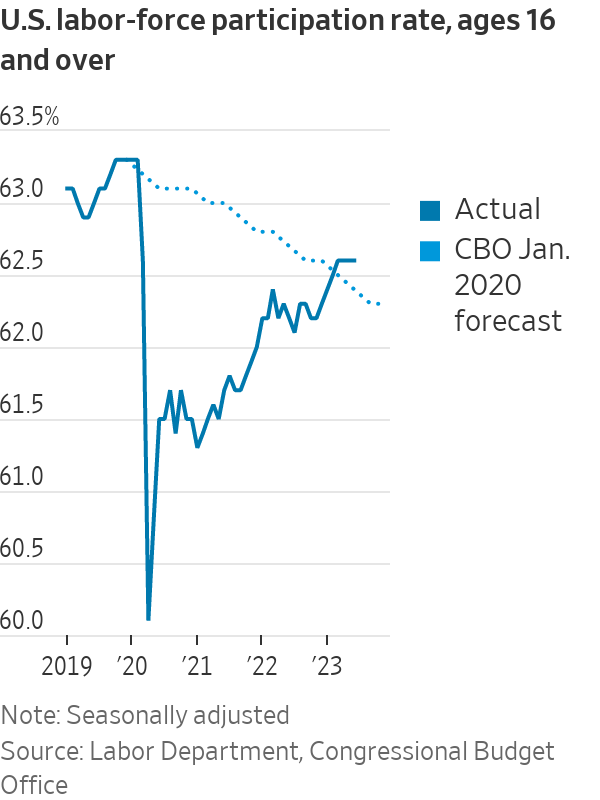
The share of the population age 55 and over in the labor force climbed steadily from the mid-1990s through the 2008 financial crisis and remained elevated for more than a decade. The Covid-19 pandemic pushed many out of the workforce, and some older workers haven’t returned, particularly those over 65.
Much of the decline in the overall participation rate was anticipated as baby boomers aged out of the workforce, but the rise in prime-age workers meant the drop wasn’t as steep.
The Congressional Budget Office in January 2020, just before the pandemic hit, forecast the overall participation rate to deteriorate steadily through the 2020s, moving down to 62.4% in the second quarter of this year.
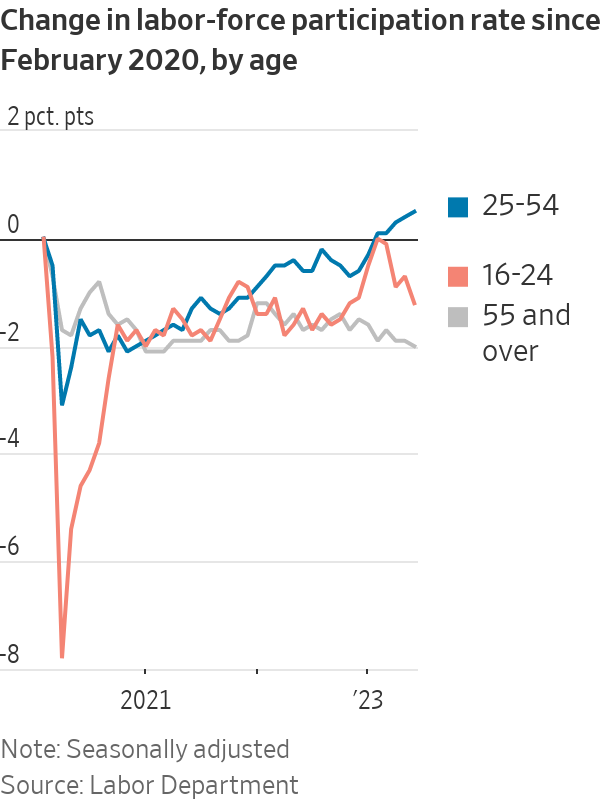
Instead, the rate was a couple of ticks higher in June at 62.6%, supported by prime-age workers.
“It seems like there is almost no cap on the supply of workers, only a speed limit on how fast we can bring them in,” Pollak said, referring to both rising prime-age participation and an influx of immigrants into the workforce.
Trends could turn if the economy cools
There are concerns that the Fed’s campaign to bring down inflation through higher interest rates will cause unemployment to rise too much and push some of the most vulnerable workers back to the sidelines.
The median forecast among Fed officials shows the unemployment rate rising to 4.1% by the end of this year and 4.5% next year from 3.6% in June, suggesting the economy will shed tens of thousands of jobs.
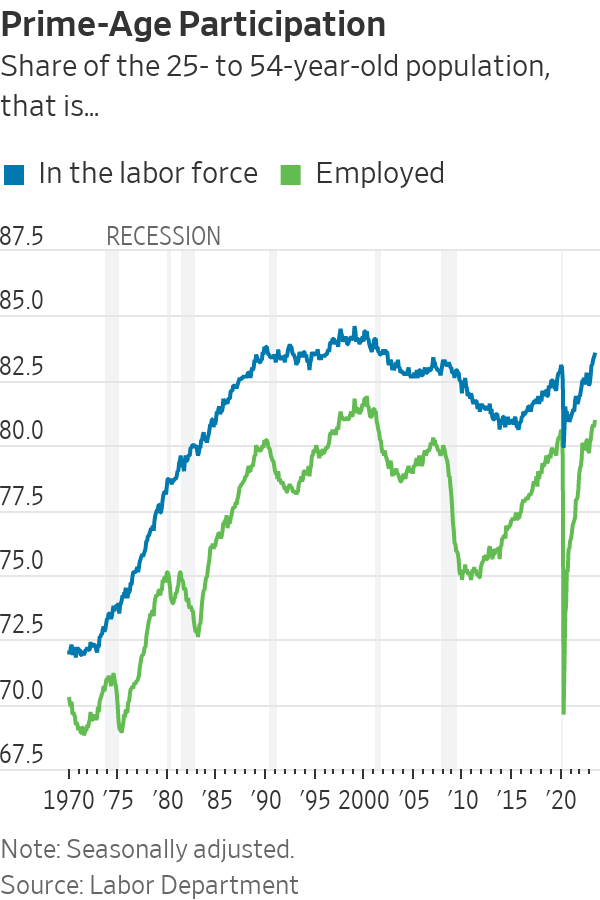
Labor-force participation tends to be cyclical, rising when the economy is strong and falling during downturns. A weaker labor market combined with structural barriers to employment could cap further gains.
With “current strength of labor demand set to fade, further progress from here will probably be more gradual,” Andrew Hunter, deputy chief U.S. economist at Capital Economics, said in a research note.
 Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Copyright 2020, Dow Jones & Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved Worldwide. LEARN MORE
Kaspersky warns that as finance goes digital, cyber risks surge — with attacks costing nearly 3x more than annual security budgets.
Qatar International Islamic Bank (QIIB) priced its $500mn five-year sukuk at T+85bps, tightening from initial guidance of T+125bps, with a 4.50% coupon and $1.85bn in orders. Issued under its $2bn Trust Certificate Programme, the sukuk will list on the London Stock Exchange, with Citi, HSBC, DIB, QNB Capital, and others as joint leads.
HAMA MEA celebrates 10 years of advancing hospitality investment across the Middle East and Africa, driving sustainability, digital transformation, and data-led collaboration to strengthen regional growth and asset performance.
Markets remained largely stable despite a tech selloff, with G10 currencies trading in narrow ranges and some emerging markets seeing modest gains. The British pound held firm after the Bank of England’s dovish stance, while the New Zealand dollar weakened on soft labor data. Investors now await a U.S. government shutdown resolution that could restore key economic data releases.
While tech stocks had their worst week since April’s “liberation day” crash, currency markets largely took the AI mini-crash in stride. G10 currencies remained in tight ranges, while some emerging market currencies posted modest gains. Amid this calmness, it is worth noting that Sterling weathered the Bank of England’s dovish turn in November well, posting modest gains against the dollar. The week’s loser was the New Zealand dollar on disappointing labor market data there. As this is written, hopes are rising for a resolution to the US Federal shutdown impasse. This would restart the release of economic data and shed much-needed light on the state of the US economy.
Enrique Díaz-Álvarez, Chief Economist at Ebury said: “Next week will be busy for Sterling, as labor market data released Wednesday is followed by third-quarter GDP and September industrial production on Thursday. Little is expected to happen in the Eurozone. Whether we receive any market-moving news about the US economy will of course depend on an agreement to end the shutdown. We will also be following developments in the stock market, as wealth effects and the impact of AI investment have probably been a net support for the US dollar.”
GBP
The Bank of England maintained rates unchanged last week, but barely, as four of the nine MPC members dissented—more than had been expected. Sterling bore this surprisingly well, rebounding after a short post-meeting downdraft. While we wait for the key November 26th budget release, this week’s economic data will be key, given the apparent data dependence of the MPC. The employment report on Tuesday and the flash GDP release on Wednesday are key. Any positive surprise on either will force markets to reprice the chances of a December cut, currently seen at 70%.
EUR
The only notable news from the Eurozone this week will be the release of the first revision to third-quarter GDP numbers. We look to it to confirm the modest improvement in the tone of economic news lately. With the ECB on hold for the foreseeable future, we continue to wait for evidence of the massive German fiscal stimulus package, announced earlier this year, to start showing up in the leading economic indicators, which may be the catalyst needed for another leg up in the euro versus the dollar.
USD
The limited privately or state-sourced data that we are still getting from the US suggests that job creation remains anemic, but layoffs remain at very low levels. Last week’s Challenger layoff report seemed to show a spike in firings, but we would heavily discount this particular data point, as it has not been a reliable indicator in the past. While the U.S. economy appears relatively undamaged by the shutdown, this could quickly begin to change if it lasts much longer. Air travel cancellations and chaos this week may be the first sign of lasting damage. We do expect the additional political pressure from this and other impacts to bring about an agreement that will restore the normal flow of data and economic reports.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
Americans now think they need at least $1.25 million for retirement, a 20% increase from a year ago, according to a survey by Northwestern Mutual
Aramco posts $28B Q3 profit, proving resilience amid oil market volatility. Despite an 11% drop in prices, strong production and cost control boosted performance — reinforcing Aramco’s global energy leadership and commitment to innovation and sustainability.
Saudi Aramco has once again demonstrated its resilience amid global energy market volatility, reporting robust third-quarter 2025 results that highlight the company’s operational strength and strategic focus on the future of energy.
The company posted an adjusted net income of USD $28.0 billion for the quarter, slightly up from USD $27.7 billion a year earlier, despite oil prices being down around 11% over the past 12 months. This performance underscores Aramco’s ability to offset softer prices through strong production levels and disciplined cost control.
Operational cash flow remained solid at USD $36.1 billion, enabling the company to maintain its hefty dividend yield of around 5%. Even as global energy markets experience turbulence, Aramco continues to generate formidable cash flows and deliver consistent returns to shareholders.
Commenting on the results, Josh Gilbert, Market Analyst at eToro, said: “Aramco’s third-quarter performance once again highlights its strength and ability to navigate challenging market conditions. Despite an 11% decline in oil prices over the past year, the company has managed to deliver steady profits through production growth and strong cost discipline. Its robust dividend yield and consistent cash flow reinforce Aramco’s position as one of the most resilient players in the global energy sector.”
Aramco also continued advancing its long-term strategy of sustainable growth and diversification. The company raised its 2030 gas output target by 80% compared to 2021 levels, with several major upstream projects progressing as planned. These initiatives reinforce Aramco’s commitment to its core hydrocarbon business while supporting global energy stability.
Beyond oil and gas, Aramco is investing in innovation and emerging technologies. In October, the company announced plans to acquire a minority stake in the artificial intelligence firm HUMAIN, positioning itself at the forefront of industrial AI applications. Additionally, Aramco expanded its downstream portfolio through a refining and petrochemical joint venture in China’s Fujian province, strengthening its international footprint.
These strategic moves reflect Aramco’s commitment to shaping a technology-driven, lower-carbon future, aligned with its goal of achieving net-zero operational emissions by 2050. Through innovation, partnerships, and investment in new technologies, the company aims to balance today’s energy needs with tomorrow’s sustainability ambitions.
While Aramco’s share price has lagged in recent years, the company’s operational performance, strategic diversification, and continued shareholder returns underscore its capacity to adapt and lead amid an evolving energy landscape.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
Interior designer Thomas Hamel on where it goes wrong in so many homes.
Egypt’s inflation likely rose to 12% in October, up from 11.7% in September, driven by fuel price hikes and higher rents, according to a Reuters poll. Despite the uptick, inflation remains far below its 2023 peak of 38%, with analysts expecting the Central Bank of Egypt to continue rate cuts this month.
Egypt’s headline inflation is expected to have risen to an annual 12.0% in October after an increase in fuel prices and a new law allowing landlords to raise rents, a Reuters poll found.
The median forecast of 14 analysts polled by Reuters was for annual headline urban consumer inflation to have risen, from 11.7% in September. The higher inflation would end a four-month-long downward trend.
Four analysts also provided predictions for core inflation, which omits volatile items such as certain food and fuel products. They predicted it would drop to a median 11.0% from 11.3% in September. The polling data was collected over November 3-6.
Sri Virinchi Kadiyala of Abu Dhabi’s ADCB, who forecast that inflation would accelerate to 12.5%, said inflation would be driven higher by rising prices for food, fuel prices, housing and utilities.
The government on October 17 increased the price of a wide range of fuel products by nearly 13%.
A new law letting landlords raise monthly rents took force in early August, applicable with the first subsequent rent payment. This means the first increases would have been reflected in September inflation figures.
M2 money supply growth, at an annual 22.9% in September, was little changed from August, central bank data showed.
Annual inflation has plunged from a record high of 38% in September 2023, helped by an $8 billion financial support package signed with the IMF in March 2024.
Slowing inflation prompted the Central Bank of Egypt (CBE) to cut its overnight lending rate by 100 basis points on October 2, following a 200-basis-point cut on August 28, the third and fourth reductions this year.
“This is unlikely to derail the anticipated November CBE rate cut, as the elevated real rate buffer offers the central bank ample room to reduce rates,” Kadiyala said.
The central bank’s monetary policy committee is scheduled to meet on November 20 to review overnight interest rates.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
Following the devastation of recent flooding, experts are urging government intervention to drive the cessation of building in areas at risk.
Kaspersky warns that as finance goes digital, cyber risks surge — with attacks costing nearly 3x more than annual security budgets.
The financial industry is rapidly advancing into a new digital era – more dynamic, intelligent, and interconnected than ever before. However, it brings not only rapid operational processes, highly personalized customer experiences, and limitless scalability, but also opens a door for cyber risks to slip through.
According to the Kaspersky IT Security Economics 2024 report, banking, financial and insurance (BFSI) organizations spend an average of $1.2 million a year on cybersecurity. While this figure may seem substantial, it pales in comparison to the cost of a major security incident – approximately $3.2 million, which is 2.7 times the annual cybersecurity budget. This underscores the reality that digitalization is unavoidable, and inadequate security measures directly increase the risk of becoming the next high-profile breach.
Kaspersky experts emphasize the following trends rewriting the rules in the financial sector:
- Open Banking APIs – The vision of customer-centric innovation is accompanied by a darker reality. Each API serves as both an opportunity and a potential entry point for malicious actors. There is no room for compromise when it comes to security and compliance.
- Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) enables rapid deployment of banking services through pre-built infrastructure. However, shared risk is a genuine concern: a breach within one partner’s system can cascade throughout the entire ecosystem, jeopardizing stability and eroding trust.
- Embedded Finance – Payments and lending functionalities integrated directly into retail applications, delivery platforms, and other services. While seamless and unobtrusive to users, these channels extend beyond traditional security boundaries. Protecting them requires a proactive approach involving continuous monitoring and comprehensive end-to-end security measures.
- Cloud Migration facilitates faster scaling, yet introduces risks such as misconfigurations, unclear responsibilities, and increased exposure. Over 25% of BFSI leaders now rank cloud adoption among their top cybersecurity concerns, underscoring the importance of robust cloud security strategies.
- Artificial Intelligence already utilized by approximately 75% of financial institutions, with an additional 10% planning to adopt soon. AI enhances operational efficiency, improves insights, and automates risk assessments. Nonetheless, it also introduces new threats, including manipulated models, synthetic fraud, and AI-driven phishing attacks, which complicate the distinction between genuine and malicious activity.
The expanding threat landscape
While innovation drives growth, it simultaneously amplifies vulnerabilities. The cyberthreat statistics speak from itself:
- Ransomware dominated 2024, making up 42% of incidents in the financial sector.
- Phishing struck nearly one in four attacks, with 24% specifically targeting banking customers.
- Human error accounted for over 25% of breaches, often from deliberate policy violations.
- Infostealers are rampant: one in fourteen infections leads to stolen card data.
But lurking behind these everyday breaches are Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) — organized, well-funded, and relentless adversaries. Groups such as Carbanak execute global campaigns worth billions, exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities and supply chain weaknesses.
The consequences of cyber incidents are tangible and costly. Last year, BFSI organizations represented 18% of all reported security incidents — more than any other sector. The repercussions range from disrupted customer services to attacks that remain undetected for weeks, eroding trust and confidence.
To stay ahead, financial organizations must adopt a comprehensive, ecosystem-based cybersecurity strategy, that would empower teams to address every threat, whether anticipated or hidden .
Step 1: Comprehensive preparation and audit. Begin with a thorough assessment of your entire infrastructure. Review existing processes, identify vulnerabilities, and address weaknesses before adversaries can exploit them. While internal teams can lead these efforts, engaging external specialists provides valuable fresh perspectives that can uncover concealed risks.
Step 2: Advanced technology deployment. Equip security teams with integrated platforms capable of monitoring and controlling all attack vectors. Rapid detection and swift response are essential, ensuring protection across the entire organization.
Step 3: Continuous learning and intelligence. As threats continually evolve, maintaining an up-to-date understanding of the threat landscape is critical. Leverage advanced threat intelligence and analytics to proactively inform and adapt your security strategy. Additionally, foster a human firewall through regular awareness programs, empowering employees to recognize phishing attempts, adhere to policies, and serve as the first line of defense.
By integrating cutting-edge technology, ongoing education, and trusted partnerships, organizations can establish a resilient, fault-tolerant infrastructure. Such an approach minimizes financial risks, ensures regulatory compliance, and guarantees uninterrupted business continuity.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
Qatar International Islamic Bank (QIIB) priced its $500mn five-year sukuk at T+85bps, tightening from initial guidance of T+125bps, with a 4.50% coupon and $1.85bn in orders. Issued under its $2bn Trust Certificate Programme, the sukuk will list on the London Stock Exchange, with Citi, HSBC, DIB, QNB Capital, and others as joint leads.
Qatar International Islamic Bank (QIIB), rated A2 by Moody’s (stable) and A by Fitch (stable), tightened the price on its $500 million five-year senior unsecured benchmark sukuk to +85 basis points over US Treasuries from initial price thoughts in the T+125bps area.
The Eurobond has a 4.50% coupon, with a 99.787 reoffer price and a 4.548% yield.
The orderbook closed at $1.85 billion, excluding JLM interest.
The Reg S sukuk will come under the Islamic lender’s $2 billion Trust Certificate Issuance Programme, rated A by Fitch.
It will be listed on the London Stock Exchange’s International Securities Market.
Al Rayan Investment, Bank ABC, Citi, Dubai Islamic Bank, Dukhan Bank, Emirates NBD Capital, HSBC, Mashreq, QNB Capital and Standard Chartered Bank are joint lead managers and bookrunners on the deal.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
HAMA MEA celebrates 10 years of advancing hospitality investment across the Middle East and Africa, driving sustainability, digital transformation, and data-led collaboration to strengthen regional growth and asset performance.
The Hospitality Asset Managers Association Middle East & Africa (HAMA MEA) celebrates ten years of shaping the region’s hospitality investment and asset management ecosystem. Established in 2015 within the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), HAMA MEA has evolved into a trusted regional voice for hotel owners, operators, investors, and policymakers across the Middle East and Africa. Over the past decade, the association has driven professional standards, investment discipline, and collaboration that have strengthened the region’s reputation as one of the world’s most dynamic hospitality investment hubs. What began as a member association has evolved into a powerful regional platform fostering transparency, education, and data-driven decision-making.
A Decade of Regional Impact
HAMA MEA has partnered with institutions such as Les Roches and the Emirates Academy of Hospitality Management to deliver immersive learning programs, including recurring Asset Management Masterclasses, leadership workshops, and mentorship initiatives. These sessions aim to build the next generation of regional hotel asset managers and strengthen governance and value creation.
In collaboration with analytics partners such as HotStats, the association has hosted regular data-led briefings covering ADR, RevPAR, occupancy trends, and pipeline dynamics. These insights have guided owners and investors in optimizing performance and capital allocation across the Gulf, North Africa, and Sub-Saharan Africa. HAMA MEA has also convened private roundtables and advisory sessions alongside major industry forums to align owners, operators, and government stakeholders on pre-opening challenges, workforce development, and sustainable growth.
By connecting investors with high-quality projects and partners, HAMA MEA has helped drive conversions, adaptive reuse, and mixed-use lifestyle developments in markets such as Saudi Arabia and Africa’s emerging corridors. Strategic partnerships with entities including Dubai FDI, DIFC, Bird & Bird, Emirates Academy of Hospitality Management, and other key industry players have amplified collective efforts to strengthen the regional hospitality ecosystem.
Commenting on the 10th anniversary, René Beil, President, HAMA MEA, said “HAMA MEA was created to quietly raise the game for owners and the profession. We bring owners, operators, advisors, academia and government around one table, listen first, and turn shared experience into practical next steps. Our work is intentionally humble, evidence-led and no egos, just useful collaboration that translates data into decisions which protect value and jobs. I’m grateful to our members and partners who share that spirit; the hotels are the headline, not us, and our job is to help the ecosystem make good decisions that stand up in the real world.”
Amit Nayak, CHA, Vice President, HAMA MEA commented “Our role is to turn market signals into asset-level action—fast and clear. We pair hard data with on-the-ground realities: pre-opening discipline, thoughtful capex, sharper F&B and steady post-opening performance. We’re students of the market who roll up our sleeves with owners and operators to pressure-test assumptions and move from insight to action. Owners don’t need noise; they need clarity—and when assets are resilient, teams are supported and guests choose our destinations again, that’s success for us.”
Looking ahead to 2025–2026, HAMA MEA is building on a decade of success with a renewed focus on resilience, sustainability, and digital transformation. The association aims to drive asset productivity through diversified revenue streams, technology enablement, and capital-efficient strategies; advance the green transition by supporting decarbonization, sustainable procurement, and utility optimization tied to financing incentives; and strengthen digital and data transformation by developing owner-aligned KPIs, automated reporting, and AI-assisted forecasting. With a growing emphasis on Saudi Arabia and Africa, HAMA MEA is also enhancing local asset management capacity to support giga-project pre-openings and cross-border investments. Additionally, the association is expanding education access through scholarships, internships, and mentorships that connect universities with ownership platforms and operating hospitality assets.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
Traders Hub launches an exclusive zero-fee trading account for UAE citizens, offering 3% bonuses, up to 1:1000 leverage, and free VPS hosting — empowering Emirati investors with smarter, faster trading.
Traders Hub, the Abu Dhabi-based global multi-asset brokerage, has announced the introduction of an exclusive trading account designed specifically for UAE citizens, reaffirming its commitment to empowering local traders and supporting the UAE’s vision for an inclusive, diversified, and innovation-driven financial sector.
This new account provides Emirati investors with a customized trading experience through enhanced conditions, zero-fee transactions, and exclusive incentives that celebrate their growing participation in the financial markets. The initiative reflects Traders Hub’s dedication to enabling greater access to professional-grade trading opportunities while reinforcing the company’s position as a key contributor to the UAE’s rapidly evolving investment landscape.
The account offers UAE nationals highly competitive trading conditions, including raw spreads, zero commission, and leverage of up to 1:1000 allowing traders to maximize performance while managing risk effectively. Clients can also take advantage of extended trading hours across select products, swap-free trading for five days, and zero withdrawal fees with unlimited free local bank transfers across the UAE, simplifying every aspect of the trading process. With a stop-out level of 30%, the account ensures an additional layer of protection during periods of market volatility.
Beyond trading flexibility, this exclusive account comes with tailored incentives that reward new and existing Emirati clients. Traders Hub has introduced a welcome bonus offering 3% (up to USD 10,000) on the first deposit, available exclusively to UAE citizens. The company also celebrates key national occasions, such as UAE National Day and Eid holidays, with seasonal promotions including double bonuses and fee waivers, ensuring Emirati traders enjoy added value throughout the year. In addition, account holders gain access to dividend adjustments on select CFD equity products, enabling portfolio diversification and greater long-term opportunities.
Recognizing that technology and speed are vital to modern trading, Traders Hub has integrated advanced infrastructure within this offering. The account provides free VPS hosting for high-volume Emirati clients, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity, faster execution speeds, and overall smoother trading performance. This reflects Traders Hub’s continued alignment with the UAE’s national priorities for digital transformation and innovation within financial services.
Accessibility and inclusivity remain at the heart of this initiative. The account is exclusively available to UAE nationals with valid Emirati passports and can be activated with a minimum deposit of USD 100. By lowering the entry threshold, Traders Hub aims to encourage both experienced traders and first-time investors to participate in the markets confidently, with the full backing of a globally trusted brokerage.
This introduction marks a significant step in Traders Hub’s broader strategy to deepen its engagement with the UAE’s investor community. By tailoring financial solutions to local needs, the company continues to contribute to the country’s ambition of fostering a well-informed and financially active population. The exclusive account also reflects the UAE’s wider vision to develop a robust financial ecosystem that balances global competitiveness with national participation.
Commenting on the launch, Hafez Baker, COO at Traders Hub, said:
“We’re proud to introduce an offering that celebrates the UAE’s trading community while creating opportunities for sustainable financial growth. This exclusive account represents our commitment to empowering Emirati investors with the tools, conditions, and confidence they need to succeed in today’s fast-moving global markets. We see this as an investment in the country’s financial future and a reflection of our long-standing partnership with the UAE’s economic vision.”
As a Category-1 regulated brokerage, Traders Hub has built its reputation on transparency, innovation, and trust. The firm serves both retail and institutional clients, providing access to forex, commodities, indices, and CFDs through a robust, technology-driven platform. By combining cutting-edge tools with localized support, the company ensures that clients in the UAE and beyond benefit from a reliable, secure, and high-performing trading environment.
Through this new initiative, Traders Hub continues to expand its role in shaping the financial future of the UAE. The exclusive offering for Emirati citizens stands as a symbol of its ongoing efforts to promote inclusivity, financial literacy, and national participation in global financial markets.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
Aldar Properties reports a record AED 6 billion profit for the first nine months of 2025 — a 30% rise year-on-year, the highest in its history. Revenues surged 43% to AED 23.6 billion, driven by record UAE property sales of AED 9.1 billion in Q3 and strong investor demand, with 77% of sales from expatriate and foreign buyers.
Aldar Properties has reported another record-breaking performance, underlining the strength of the UAE’s property market and investor confidence in Abu Dhabi’s real estate sector. The developer posted a net profit after tax of AED 6.0 billion for the first nine months of 2025, marking a 30% year-on-year increase, and the highest in its history—achieved despite growing tax obligations.
Revenue for the period rose 43% to AED 23.6 billion, as nearly every part of Aldar’s portfolio delivered strong returns. In the third quarter alone, net profit climbed 49% year-on-year to AED 1.9 billion, supported by solid property sales and continued rental income growth.
Commenting on the results, Josh Gilbert, Market Analyst at eToro, said: “Aldar’s latest earnings are another sign that the UAE’s largest developer is firing on all cylinders. The company’s ability to combine high-growth development sales with a robust recurring income base makes its business model stand out in today’s market. This double-digit growth is a key reason why Aldar’s shares have rallied this year.”
Aldar’s development business was a standout performer, recording AED 9.1 billion in UAE property sales during Q3—its highest quarterly sales ever—driven by strong demand for new project launches and available inventory. Notably, overseas and expatriate buyers represented 77% of Aldar’s UAE sales during the first nine months of the year, reflecting Abu Dhabi’s growing appeal as a safe-haven investment destination.
This demand has lifted Aldar’s development revenue backlog to a record AED 66.5 billion, securing visibility on future income for the coming years. Meanwhile, the company’s investment portfolio continues to expand, with recent acquisitions—including commercial assets in Masdar City—already contributing to revenue growth.
Flagship destinations such as Yas Mall also reported double-digit increases in tenant sales and footfall, underscoring the strength of Abu Dhabi’s retail and tourism recovery.
“What we’re seeing from Aldar is an exceptional balance between growth and stability,” added Gilbert. “The company is executing well on its long-term strategy, boosting property sales while expanding its base of recurring revenues. For investors, this latest report confirms that Aldar’s growth story still has plenty of room to run.”
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
J.P. Morgan’s 2026 Long-Term Capital Market Assumptions mark 30 years of research, projecting a 6.4% return for 60/40 portfolios and 6.9% with alternatives. The report highlights resilience amid AI innovation, economic nationalism, and fiscal shifts, emphasizing diversification and active management to build future-ready portfolios.
J.P. Morgan Asset Management today released its 2026 Long-Term Capital Market Assumptions (LTCMAs), providing a comprehensive 10-15-year outlook for returns and risks across asset classes as the forces that drove volatility in recent years abate.
George Gatch, CEO of J.P. Morgan Asset Management comments, “J.P. Morgan is differentiated by the longevity and long-term perspective that we bring to our active management. With 30 years of producing Long-Term Capital Market Assumptions, we consistently offer essential guidance to clients ranging from institutional investors to high-net-worth individuals. As our clients face a rapidly evolving investment landscape, the LTCMAs share the insights of over 100 experts, equipping them to build resilient portfolios in an era of moderate growth, rising economic nationalism, and rapid AI-driven innovation.”
In this 30th edition of the LTCMAs, the forecast annual return for a USD 60/40 stock-bond portfolio over the next 10–15 years remains attractive at 6.4%. Even after a year of strong equity market gains, asset return projections remain robust. Although labor constraints weigh on the long-term growth outlook, we believe AI adoption will provide a near-term boost to profits and a longer-term boost to productivity. The report spotlights the opportunities to boost diversification through global equities and alternatives, particularly real assets. For investors embracing a 60/40+ portfolio, with 30% in diversified alternatives, the projected return jumps to 6.9% and the Sharpe ratio gets a 25% lift over the simple 60/40 approach.
“Our 30th anniversary Long-Term Capital Market Assumptions reflect on three decades of market evolution and look ahead to a future shaped by technology, shifting policy, and new asset classes,” said John Bilton, Head of Global Multi-Asset Strategy, J.P. Morgan Asset Management. “The economic landscape is shifting palpably. But, in our view, much of what worries investors today will ultimately pale beside the silver linings we see breaking through over the long run.”
“The global economy is adapting to a new set of realities, with fiscal activism, technological adoption, and demographic shifts driving both challenges and opportunities,” said Dr. David Kelly, Chief Global Strategist, J.P. Morgan Asset Management. “While growth in developed markets is expected to moderate, robust investment and productivity gains—particularly from AI—support a constructive long-term outlook.”
“For investors today, building resilience means going beyond the traditional. Investors need to think outside the box, embracing alternatives and real assets to manage risk and unlock new sources of return,” said Grace Peters, Global Co-Head of Investment Strategy for J.P. Morgan Private Bank. “Most importantly, anchoring your investments to a goals-based plan ensures your portfolio stays aligned and adaptable, so you can remain confident no matter how uncertain the environment.”
Key findings include:
- Resilience in markets despite slower growth: Despite a dip in growth projections due to changing labor market dynamics, asset return projections remain strong.
- Economic Nationalism is a challenge, not a showstopper: Trade frictions are making headlines, but also forcing some countries to boost domestic investment – a clear silver lining to the impact of tariffs.
- Technology continues to drive this bull market: Capital investment and technology spend continue to provide momentum for the broader market. Governments are stepping up, unleashing record stimulus and incentives.
- The AI boom is at a critical juncture: Adoption is surging, and investment is massive. Investors should pivot their attention to who will be the eventual winners and losers of new technologies, making active management key.
- Equity strength, but currency matters: After two years of 20% gains followed by another 14% so far this year, US equity performance has been exceptionally strong for USD-based investors. That said, EUR-based investors have been handed a double-edged sword, as the strength of the currency offset a very respectable rate of return from US stocks.
- Diversification isn’t optional, it’s essential: shifting policies and higher investment mean more volatile inflation. This demands smarter portfolios that use alternatives and real assets for resilience and returns. Manager selection is key to take advantage of this current environment of disruptive change.
The report also outlines the following asset class return assumptions:
- Fixed Income
- U.S. intermediate Treasuries are expected to return 4%, while long Treasuries are expected to return 4.9%.
- U.S. investment grade credit is forecast to return 5.2%, with spreads tightening due to a shortening of the maturity of debt issuance.
- U.S. high yield credit is expected to return 6.1%, with a fair value spread of 475bps, driven by higher credit quality.
- Equities
- U.S. large cap equities are expected to return 6.7%, holding steady from last year as the move from tech adoption to tech deployment broadens to other sectors and concerns over index concentration are expected to dissipate. The U.S. looks likely to remain the global leader in technology origination.
- Global equities are projected to return 7% (USD), with non-U.S. markets offering more attractive cyclical starting points and benefiting from currency appreciation.
- Emerging markets equities are expected to return 7.8% (USD), dipping modestly after strong performance this year.
- Alternatives
- Private Equity: The return assumption for private equity is 10.2%, reflecting a slight increase due to a more favorable exit environment and higher growth opportunities in technology and AI.
- Real Estate: U.S. core real estate is expected to return 8.2%, driven by attractive entry points and higher yields. European core real estate is forecast to return 6.9%.
- Infrastructure: Global core infrastructure is projected to return 6.5%, reflecting the essential nature of the services provided by this asset class through a shifting trade policy environment.
- Commodities: The return assumption for broad basket commodities remains at 4.6%, with the energy transition and geopolitical risks influencing the outlook. Gold is expected to return 5.5%, an increase from last year at 4.5%.
- Timberland: Global timberland is expected to return 6.3%, reflecting an increase from last year at 5.3%.
Three Decades of LTCMAs: From Spreadsheet to Global Standard
Celebrating its 30th anniversary, the LTCMAs reflect on three decades of extraordinary market evolution, including the internet revolution, the birth of the euro, the global financial crisis, quantitative easing, the pandemic, and the dawn of artificial intelligence.
What began as a modest spreadsheet for asset allocation has transformed into a globally relied-upon program, built on a rigorous research process that combines quantitative and qualitative insights from over 100 industry-leading portfolio managers, research analysts, and strategists worldwide.
Today, these time-tested projections cover more than 200 assets across 20 currencies, setting the standard for strategic asset allocation and long-term investment planning in an ever-evolving financial landscape.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
Saudi Arabia’s capital markets are booming, with record bond and IPO activity fueling Vision 2030’s investment drive and advancing diversification beyond oil.
Saudi Arabian capital markets are on a tear this year, with the number of bond and equity deals on course to break all records as capital pours into the country to finance trillions of dollars of investments in new cities, new industries – and (in theory at least) a new economy no longer dependent on oil.
Bond markets have led the charge, with 76 deals this year, up 77% on last year’s already record tally. The amount raised has surpassed US$70bn, which is up 40% on this point a year earlier, after US$20bn of deals from the Saudi government and US$8bn from oil giant Saudi Aramco.
Equity markets have also been on a roll, with 29 IPOs – a record for this point in the year – raising US$3.6bn amid a frenzy of buy orders. The US$1.1bn listing in May of airline Flynas was covered 100 times and the US$520m IPO of developer Umm Al Qura in March was covered 200 times.
While loan volumes are down on last year’s record, there has been some solid deal activity such as the US$7bn facility signed in January by Saudi sovereign wealth fund, Public Investment Fund.
As a result of all this activity, investment banks are set for a bumper haul in fees, with senior bankers pointing to Saudi as a particular highlight during a year that started slowly but has since taken off.
Critical role
Capital markets are slated to play a critical role in meeting the ambitious targets of the country’s transformational Vision 2030 program, announced amid much fanfare almost a decade ago. Moody’s predicts US$2trn of investment will be needed over the next four years if the country is to meet those goals.
“A growing economy and the financial demands of the mega projects underway are hoovering up cash faster than the domestic system can supply it,” said Nick Smallwood, a strategist at M&G, who says the country’s banking system is struggling to keep pace with the scale of investments.
It is little wonder given the size of some Vision 2030 projects. Neom, a futuristic city on the Red Sea, is projected to cost US$8.8trn to build, assuming it actually happens – 25 times the annual government budget. With demand for loans rising faster than deposits, banks are increasingly borrowing from abroad to keep up.
“The KSA complex is structurally increasing its reliance on international debt markets,” said Smallwood. “Banks are taking an ever greater share of Saudi issuance. KSA is therefore increasingly dependent on international investment to fund its domestic priorities.”
Acutely aware of the need to attract more capital, the country has signed multiple deals over recent months with the likes of BlackRock, Franklin Templeton, Goldman Sachs, Macquarie and State Street to unlock inflows. It has also broken into new markets, with bonds in euros, sterling and the green market.
Financial market instruments that are common in other countries but rarely or never seen in Saudi have also been launched. PIF launched a commercial paper program in June, while the Saudi Real Estate Refinance Company in August printed the country’s first ever residential mortgage-backed security.
Slow progress
But progress has not been as fast as hoped. When Vision 2030 was launched, there was talk of 150 state-owned companies being privatized, unlocking US$300bn for Vision 2030-linked investments. Huge excitement followed 2019’s record US$29.4bn IPO of Aramco – but the pipeline quickly dried up.
Years later, IPO activity has picked up but many deals have traded down sharply, indicating ongoing liquidity issues. Tellingly, the market capitalization of exchange operator Tadawul has actually fallen over the last three years, despite the surge in listings.
On the bond side, progress in expanding the market has also been slow – and dominated by government or quasi-government issuers. Last year, PIF and Aramco accounted for about 80% of all non-financial corporate issuance. Barely any private non-financial companies are tapping bond markets.
“An acceleration of cumulative private sector investment will be required by 2030 to sustain growth momentum,” said Aziz Al Sammarai, an analyst at Moody’s, who added that the need to finance projects like World Expo 2030 and FIFA World Cup 2034 should boost issuance.
“Strategic investments across sectors is likely to spur an increase in equity and debt issuance. Increased capital market activity will, over time, deepen Saudi Arabia’s financial markets, broaden investor participation and support the development of a more diversified and resilient funding base.”
Deals with financial institutions to attract further liquidity and deepen the country’s capital markets also continue. Last month, Saudi Arabia was added to a JP Morgan bond index, in a deal that could attract around US$5bn of foreign inflows into its sukuk and bond markets.
PIF announcement
A catalyst for further activity could be just around the corner. PIF, which is driving much of the Vision 2030 agenda, including privatization of government assets and incentivizing private sector investment, is expected to announce a big “update” very soon.
“In the coming two months or so we will set the new strategy for PIF, which is a continuation from the original one … from 2030 all the way to 2040 and beyond,” chairman Yasir Al-Rumayyan told a Washington event last month. The announcement could lead to greater clarity – and more privatizations.
The clock is ticking. Oil revenues have fallen by about a third from their peak, and the US$200bn they contribute to the public purse is not enough to balance the books. The government has run a deficit in 10 of the past 11 years, despite its vast oil wealth, and is on course to run a larger-than-expected deficit this year.
If it is to wean itself off oil and create a more sustainable, diversified economy then broadening access to capital markets will be key.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
Gold prices rebounded above $4,000 per ounce as a weaker dollar and expectations of Fed rate cuts lifted demand, offsetting optimism over U.S.-China trade talks. Spot gold rose 0.7% to $4,009, extending this year’s 53% rally after hitting a record $4,381 in October.
Gold prices regained some lost ground on Tuesday, rising above the $4,000-per-ounce level as a weaker dollar and expectations of further Federal Reserve rate cuts outweighed pressure from signs of a thaw in U.S.-China trade tensions.
Spot gold was up 0.7% at $4,009.39 per ounce, as of 0141 GMT, after dropping more than 3% on Monday to its lowest level since October 10. U.S. gold futures for December delivery rose 0.1% to $4,022.10 per ounce.
“Buyers who were waiting on the sidelines for gold are now being tempted into taking positions at these price levels. Also, we are seeing a bit of softness from the dollar, which is giving gold a reprieve,” said KCM Trade Chief Market Analyst Tim Waterer.
The dollar index was down 0.1% against its rivals, making gold less expensive for other currency holders.
On Sunday, top Chinese and U.S. economic officials hashed out the framework of a trade deal for U.S. President Donald Trump and his Chinese counterpart Xi Jinping to decide on later this week.
Trump said he thought a deal would be reached with China, and announced a flurry of deals on trade and critical minerals in Malaysia with four Southeast Asian nations during the first stop of his five-day Asia trip.
“If Trump and Xi have a productive meeting on trade this week, this could leave gold swimming against the current to some degree. But this could be offset if the Fed delivers a dovish tone with the expected rate cut this week,” Waterer said.
With the Fed widely expected to cut interest rates at the end of its policy meeting on Wednesday, investors are awaiting any forward-looking language from Fed Chair Jerome Powell.
Meanwhile, the European Central Bank and the Bank of Japan are both broadly expected to hold rates steady later this week.
Gold prices have gained about 53% this year, reaching an all-time peak of $4,381.21 on October 20, bolstered by geopolitical and economic uncertainties, rate-cut bets and sustained central bank buying.
Elsewhere, spot silver fell 0.3% to $46.74 per ounce, platinum slipped 1.2% to $1,571.85 and palladium dipped 0.8% to $1,391.15.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
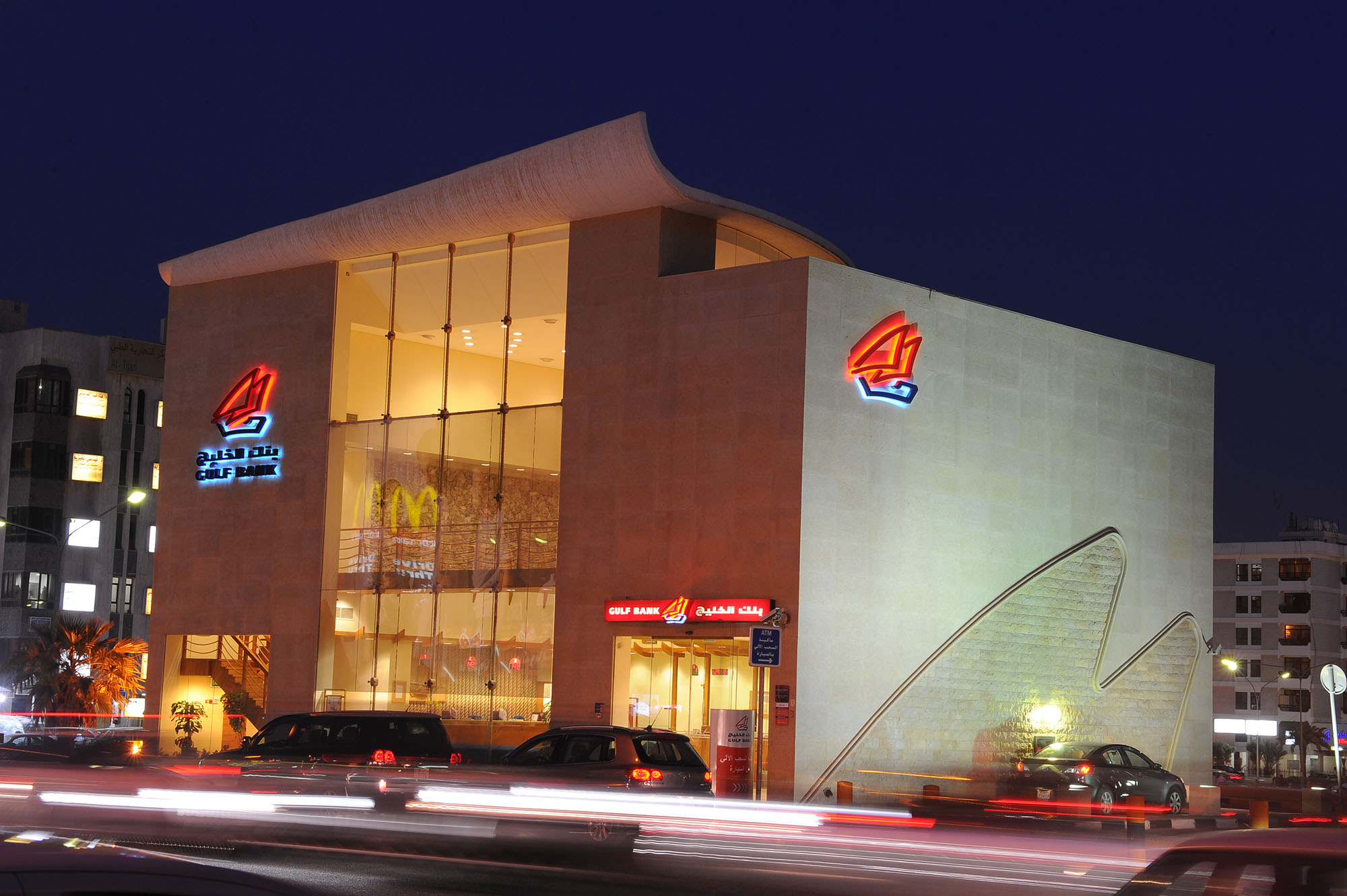
Gulf Bank won the “Best Next Generation Program” award at the 2025 MEED Banking Excellence Awards in Dubai, recognizing its innovative banking solutions that empower young entrepreneurs and next-generation investors across Kuwait.
Gulf Bank announced that it has received the “Best Next Generation Program” award as part of the 2025 MEED Banking Excellence Awards for Wealth Management and Private Banking in the Middle East and North Africa, organized by the international publication MEED in Dubai.
This award comes in recognition of Gulf Bank’s efforts to develop innovative banking programs designed for young entrepreneurs and promising business owners, by providing specialized financial and advisory solutions that enable them to grow their businesses and build a sustainable financial future.
Gulf Bank was selected for this prestigious award based on a range of professional criteria, including the design of innovative financing and advisory programs tailored for young and emerging entrepreneurs, the launch of flexible banking products and digital services that elevate the next generation’s customer experience, and the bank’s leadership in digital transformation, exemplified by its advanced mobile application.
The Bank was further recognized for the development of its premium private banking services, offering asset-backed financing, exclusive investment solutions, and elite banking cards designed to meet the needs of high-net-worth clients.
Commenting on this achievement, Abdulrahman Al-Khubaizi, Deputy General Manager of Consumer Banking – Wealth Management at Gulf Bank, stated: “We are honored to receive this prestigious award, which reflects our unwavering commitment to empowering Kuwaiti youth and supporting them in building their businesses and securing their financial future. This recognition not only celebrates our achievements but also reinforces our responsibility to continue innovating and fulfilling the aspirations of the next generation.”
Al-Khubaizi added that Gulf Bank continues to place strategic focus on its private banking services, offering tailored programs and initiatives designed for young high-net-worth individuals and future investors. He emphasized that the Bank remains dedicated to expanding its client base and strengthening customer loyalty, contributing to sustainable growth and long-term value creation in the years ahead.
He further noted that the bank is committed to providing high-quality, bespoke wealth management services, through personalized banking solutions that align with clients’ needs and lifestyles. This approach ensures seamless banking experiences and attracts more affluent clients seeking exclusive and refined banking services.
It is worth noting that Gulf Bank recently received the “Best Customer Experience in Private Banking Services” award at the Private Banker International Global Wealth Awards 2025, one of the world’s leading awards in the wealth management sector.
In 2024, Gulf Bank was also honored with the “Best Next Generation Offering for Emerging High-Net-Worth Clients” award from the same organization, further reaffirming its leadership in addressing the evolving needs of clients, particularly the new generation of investors.
MEED, the organizer of this award, is a renowned media and business intelligence platform established in 1957, dedicated to tracking and analyzing economic and financial developments across the Middle East. The organization hosts the MENA Banking Excellence Awards in collaboration with leading global banking partners, including Private Banker International, to honor financial institutions that exemplify excellence in innovation, customer experience, and digital transformation.
The awards are widely regarded as among the most prestigious recognitions in the regional banking sector, distinguished by transparent evaluation criteria and a rigorous selection process conducted by a specialized judging panel of international banking experts and consultants.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
Alexandre de Betak and his wife are focusing on their most personal project yet.
Nolte Küchen, Germany’s leading premium kitchen brand, is expanding in the UAE under its new entity Nolte UAE, investing AED 25 million to launch a flagship showroom by 2026 and strengthen its direct presence — reaffirming its “Made in Germany” quality, innovation, and sustainability.
Nolte Küchen, Germany’s leading premium kitchen brand, is strengthening its presence in the Middle East as part of a renewed global growth strategy rooted in German design excellence and craftsmanship. Having been present in the UAE market since 2007 with Universal Trading Company (UTC), in a mutually agreed step to further ensure market development and expansion. The brand will now transition to a direct-to-consumer model under its new mainland entity, Nolte UAE.
As part of this expansion, Nolte Küchen will invest over AED 25 million in the coming years. This includes the launch of a flagship showroom on Sheikh Zayed Road by early 2026, and the establishment of a dedicated team of engineers, designers, and architects offering end-to-end kitchen solutions defined by German precision and quality standards. The move underscores Nolte Küchen’s confidence in the UAE’s role as a regional hub for design and innovation, as well as a key market in the company’s international expansion. It strengthens its direct relationships with both B2B and B2C customers through greater brand consistency, service excellence, and competitive pricing.
The UAE’s premium kitchen market has nearly doubled since 2020 and is projected to reach US$200 million by 2030, reflecting sustained demand for high-quality European design. The brand’s continued expansion aligns with this growth, positioning Nolte Küchen to meet evolving customer expectations through faster delivery timelines, improved service, and an expanded product range that includes Nolte Küchen, Nolte Neo, Express Kitchen, and Living & Spa. The brand’s mission remains to bring “Made in Germany” quality, design excellence, and innovation to every home, while catering to diverse market segments across both private and professional customers.
Selva Kumar Rajulu, Managing Director of Nolte UAE, said: “Since establishing Nolte FZE in the region in 2011, we have built a strong legacy rooted in innovation and trust. This new phase, as Nolte UAE, enables us to engage more closely with customers and partners, ensuring every project reflects German design excellence. The UAE has always been central to our journey, and this expansion reinforces our commitment to the market and its role in driving our global presence across high-growth international markets.”
In the Middle East, Nolte Küchen’s presence is anchored by its regional competence centre in Dubai, which oversees markets across 30 countries and have managed to deliver more than 80,000 project kitchens and 35,000 retail kitchens in the last years. Supported by over 75 branded showrooms across the Middle East, Asia, and Africa, the Dubai hub delivers landmark developments such as Tilal Al Ghaf and Harmony Villas in Dubai, MERED’s Iconic Residences design by Pininfarina in the UAE, Rafal Residence in Riyadh, and Al Mouj in Muscat, along with large-scale residential and hospitality projects in Qatar, Jordan, and Kuwait. This regional infrastructure enables the brand to serve both developers and homeowners with scale, precision, and local expertise.
Beyond aesthetics, Nolte Küchen has earned the title of Germany’s most popular kitchen brand, recognised for its superior product quality, design innovation, and customer satisfaction by the German Institute for Service Quality over several years. The company offers one of the world’s widest range of finishes, materials, and configurations, with customisation options that set a global benchmark of personalisation in kitchen design. It also holds the distinction of being the world’s most sustainable kitchen brand, maintaining a 100% production base in Germany and the industry’s first independent sustainability report.
The UAE’s Net Zero by 2050 strategy and Estidama Pearl Building Rating System encourage developers and manufacturers to adopt more sustainable construction and design practices. Nolte Küchen is the only German kitchen brand with both FSC and PEFC certifications, reflecting its commitment to long-term environmental responsibility. The brand also releases annual sustainability reports, highlighting its continued investment in responsible production and transparency.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
Sydney’s prestige market is looking up, here’s three of the best on the market right now.
Emirates NBD to acquire a 60% stake in India’s RBL Bank for $3 billion, marking the largest cross-border deal in India’s financial sector and reinforcing the UAE bank’s expansion across high-growth markets.
Middle Eastern bank Emirates NBD will buy a 60% stake in Indian private lender RBL Bank for $3 billion, in the largest cross-border acquisition in India’s financial sector.
Emirates NBD will invest 268.53 billion Indian rupees ($3.05 billion) in the bank through a preferential issue of shares, RBL Bank said in a statement to exchanges.
The deal is among a series of cross-border deals in India this year, and comes months after Japan’s Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation’s move to buy up to 25% of Yes Bank.
UAE banks have also been considering cross-border expansions in the region and further afield. Both ENBD and Abu Dhabi’s FAB have been expanding their presence in markets like Saudi Arabia and Egypt.
TAPPING INDIA’S FAST-GROWING FINANCIAL SECTOR
“This investment reflects ENBD’s confidence in India’s fast-growing financial sector, reinforcing India’s strategic importance within the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor,” the banks said in a joint statement after the deal was announced.
The lender, which is entirely owned by retail shareholders and investment funds, said the deal is subject to regulatory approvals.
India allows 74% foreign investment in private banks but limits shareholdings of any single foreign institution to 15% unless regulator the Reserve Bank of India grants an exemption. The RBI has informally communicated its backing for the ENBD deal, Reuters has reported.
As part of the deal, Emirates NBD will also launch an open offer for additional shares from retail shareholders in line with India’s takeover regulations. They will be offered at 280 rupees per share, according to an investor presentation by RBL Bank.
As per these rules, an acquisition of more than 25% shares in a company requires the acquirer to offer to buy another 26% from retail shareholders.
Emirates NBD will ensure its shareholding does not go beyond the overall 74% foreign investment limit, the exchange announcements from both banks said.
The Dubai-based lender will be designated the “promoter” of RBL Bank, a regulatory classification in India used for large shareholders with management control. It will also have the right to nominate directors to the RBL Bank board, subject to regulatory approvals.
Anand Dama, head of financial sector research at Mumbai-based brokerage Emkay Global Capital Financial Services, said the acquisition “will open up flood gates for more such investments into small- and mid-sized banks in the country”.
PAN-INDIA PRESENCE
RBL Bank’s former CEO Vishwavir Ahuja resigned abruptly in 2021 after the Indian central bank appointed an additional director to its board – a step typically taken to increase scrutiny on a bank.
Since then, the bank has seen a management change and earnings have stabilized. Its stock has soared 90% so far in 2025 against an 8% gain in India’s benchmark Nifty 50 index.
As of March 2025, RBL Bank had assets of 1.46 trillion Indian rupees ($16.61 billion), making it the 13th largest of 21 private banks in the country.
The lender has 15.17 million customers and a network of 562 branches across 28 Indian states and union territories.
“The infusion will significantly strengthen RBL Bank’s balance sheet, enhance its Tier-1 capital ratio, and provide long-term growth capital,” the banks said in the press release.
Investors will watch to see if a combined Emirates NBD-RBL Bank, with so much capital at its disposal, would look at more acquisitions in banking, Dama said.
Emirates NBD, which is majority-owned by Dubai’s government, had assets worth $297 billion as of end-June. Together with other UAE banks, it has benefited in recent years from rising demand for credit and government-driven investment in non-oil sectors.
It has operations in countries including Egypt, Saudi Arabia and Turkey, where it acquired DenizBank in 2019.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
Egypt submits a new state offering program to the IMF, featuring major divestments in renewables, finance, logistics, and airports, as part of its economic reforms — with plans to cut debt to 75% of GDP and attract $2.5B in global investments.
Egypt has submitted a new state offering program to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) as part of its ongoing economic reform efforts, Minister of Finance Ahmed Kouchouk told Al Arabiya Business.
Kouchouk said the program focuses on three to four major offerings during the current fiscal year (FY) in the financial, insurance, airports, renewables, and logistics fields.
He added that a major divestment deal will be announced soon, referring to anticipated transactions in the renewable energy, communication data centers, and mobile towers sectors.
Kouchouk noted that a new debt management strategy will be unveiled in December, focusing on extending the average debt maturity.
The minister confirmed that the government debt has been reduced by nearly 10% of gross domestic product (GDP) within two years, reaching 85% now, with a goal to bring it down to 75% within three years.
He also said Egypt is in talks with Kuwait, Qatar, and several European countries to convert part of its debt into investments, though discussions remain in early stages.
Additionally, Kouchouk mentioned that Egypt still has a chance to attract $2.5 billion in international bonds until next June.
He further confirmed that the fifth and sixth IMF program reviews will be integrated into the current economic reform framework.
According to the IMF’s latest World Economic Outlook, the fund raised its forecast for Egypt’s real GDP growth in FY 2025/2026 to 4.5%, up from its July estimate of 4.1%.
Chris Dixon, a partner who led the charge, says he has a ‘very long-term horizon’
Self-tracking has moved beyond professional athletes and data geeks.
























































































